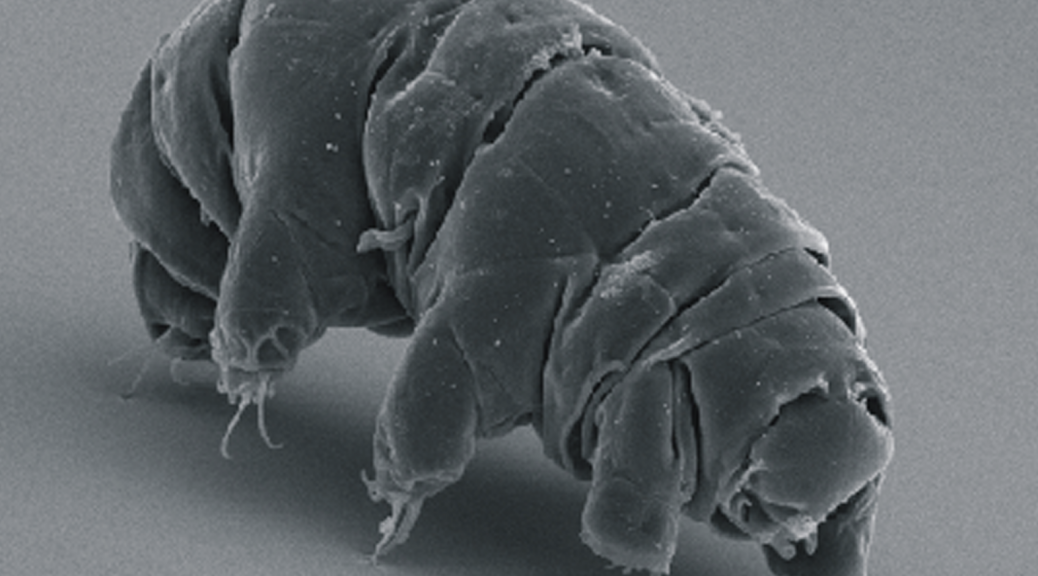
There are some animals that astound us by their oddity: the “duck-billed” platypus because it lays eggs, the sea horse because the male broods the young, the ant lion because it digs pits that entrap ants. Tardigrades beat them all, different in so many respects scientists scarcely know where to fit them in on the evolutionary family tree. They are like aliens, come from another galaxy far away.

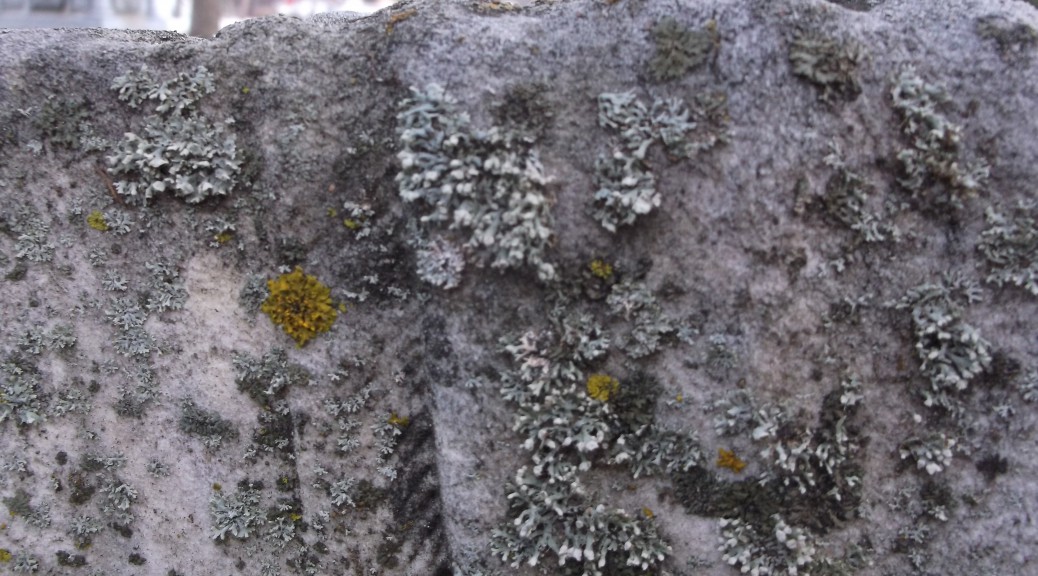
Sometimes called water bears, they lumber about on eight clawed legs, looking ungainly and a bit loveable with their antics. Possessing odd mouthparts with sharp stylets that pierce the plants upon which they feed, they suck out cell contents as if with a straw. Did I mention that they love mosses and lichens—and that they require a microscope to be seen?
I have encountered them twice in my career. First, long ago, I took a course in mosses. Upon immersing those organisms in water to rehydrate them, tardigrades associated with them spring back to life, too: like instant coffee, you just add water to get the thing you want (in this case, a living being).
The other time I saw them was at the beach when I would dig holes near the water’s edge and watch them fill up with water. Upon examining that water under the microscope, I discovered enormous numbers of water bears. My research tells me that, in addition to mosses, they eat algae and one-cell creatures, too. If they can be found among the grains of sand at a beach, no doubt they can be found in many other unsuspected places all around us.
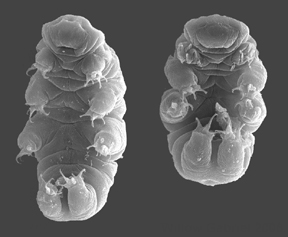
Besides being cute, tardigrades are known for their resilience. They can be dehydrated and pop back to life after years in dormancy; they can be frozen to absolute zero, the temperature of outer space, and resume their normal lives without an iota of stress or worry; they can be boiled, scarcely feeling the heat. In short, they appear to be super-animals.
If you wish to see water bears, do what I did: rinse a clump of moss with water, allow the washing water to settle and then use a medicine dropper to suck up some debris. Surely, through your microscope you will see the creatures lumbering about in search of food or a mate. If you do not wish to take the trouble to corral your own animals, you may visit this web site to study them second-hand:





